Constantrate infusions part two Vet Times
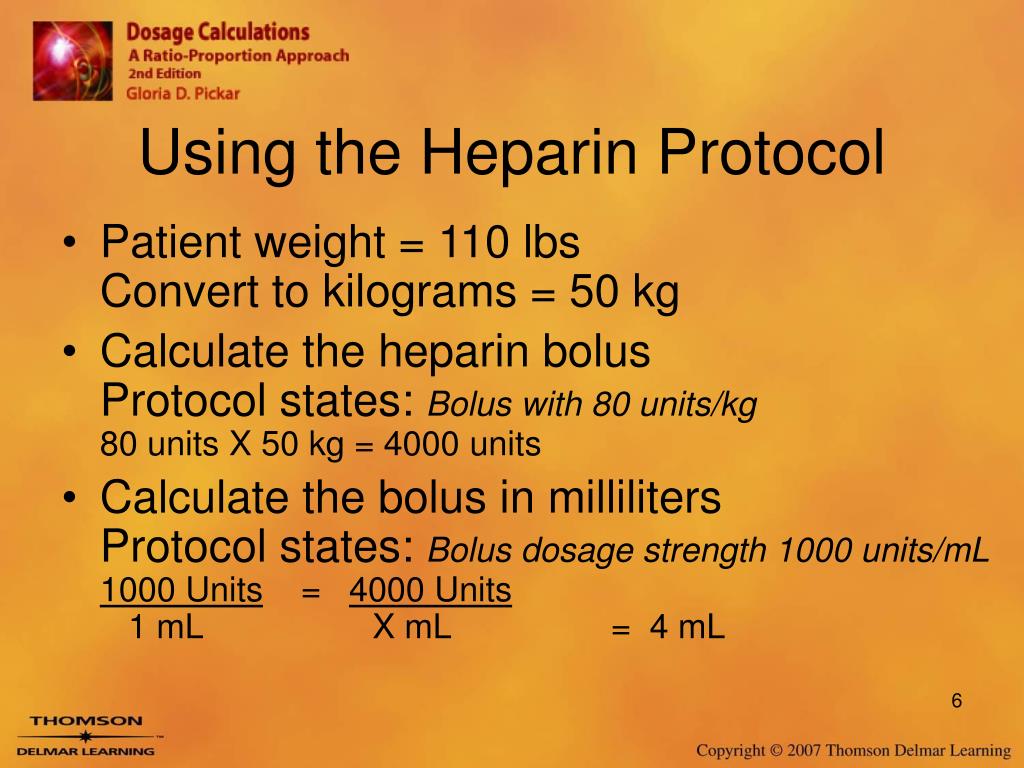
First convert pounds into kilograms by dividing pounds by 2.2 (there are 2.2 pounds per kilogram): 11 pounds/ 2.2 pounds per kg (pounds cancel out) = 5 kg Now take the kg and multiply by the dose: 5kg X 2 mg/kg/day (kg cancel out) = 10 mg/day Now divide by the number of hours in a day (24) to get the per hour rate:

Dopamine drug calculation formula for nurses Infusion rate calculation 2020 YouTube
A collection of drug calculators for Veterinarians and support staff. Calculators for Emergency and Anesthetic drugs, Constant Rate Infusions (CRI), IV Fluid Rates, Chocolate Toxicity, Calorie requirements for dogs and cats and Unit conversion (including Weight, Temperature, Body Surface Area, mg to ug, cc's to ounces's, cm's to inches). Also includes normal laboratory reference ranges for.
Constant Rate Infusion Preparation YouTube
Summary Equipment and medications that can be used for constant rate infusion are growing in popularity in small animal practices. This means the veterinary nurse will need to be able to calculate these accurately and efficiently to avoid accidental over or underdose.

How to calculate and manage constant rate infusions The Veterinary Nurse
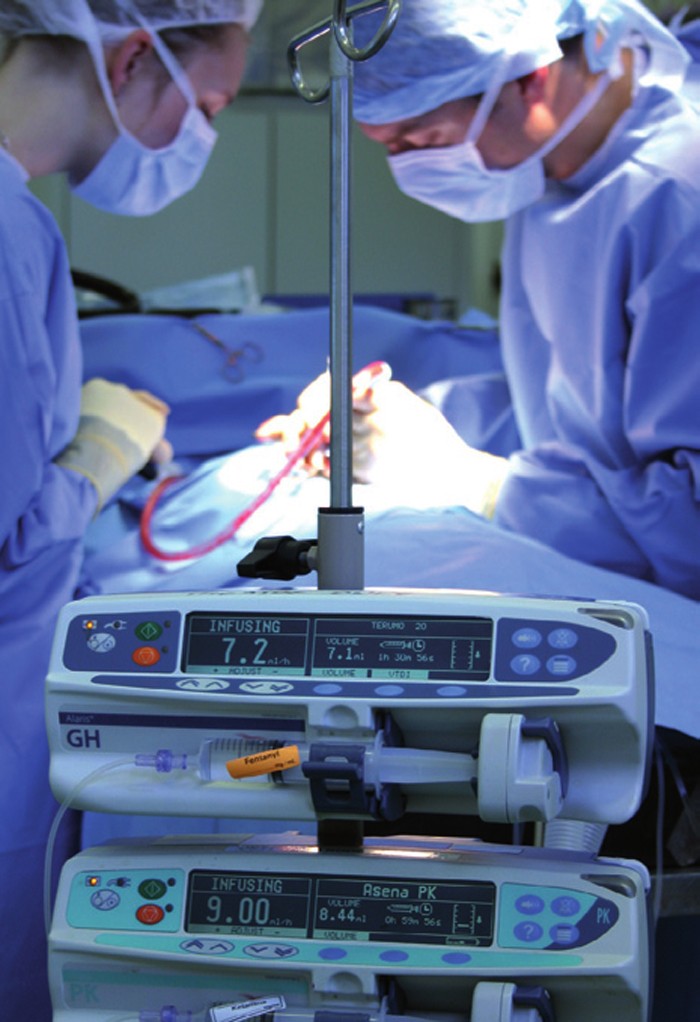
Constant rate infusions (CRIs) are a simple, flexible, and inexpensive way to administer intravenous medications to hospitalised and surgical patients. They are administered using standard fluid pumps or with syringe drivers (either electronic or spring loaded), and many medications can be added to a patient's pre-existing intravenous fluids.

How to calculate and manage constant rate infusions The Veterinary Nurse
A constant rate infusion/manually controlled infusion (CRI/MCI) of analgesic drugs is a simple and effective means of improving patient comfort. Various formulations can be used as a constant rate infusion; the protocol chosen depends on the patient and the degree of pain experienced or anticipated.
PPT Advanced Adult Intravenous Calculations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID393773
A constant rate infusion (CRI) is prepared to give a patient a continuous dose of drug in intravenous (IV) fluids. This method is advantageous for administering continuous pain management or for drugs with a short half life, as the drug is maintained at effective plasma concentrations for the duration of the CRI ( Creedon et al, 2012 ).

How to calculate and manage constant rate infusions The Veterinary Nurse
Calculating CRI Doses Imagine that you have a 10 kg dog in need of a 10 ug/kg/min CRI of lidocaine. The concentration of lidocaine is 20 mg/ml. How can you use this information to treat your patient? First, multiply the dose by the dog's weight, like you would do if calculating any other drug dosage.

PPT IV Administration Dosage Calculation PowerPoint Presentation ID4497697
Practical How to calculate and manage constant rate infusions Megan Brashear Published Online: 31 Jul 2015 https://doi.org/10.12968/vetn.2015.6.6.354 Share Abstract A constant rate infusion (CRI) is a medication continuously administered to a patient and is used to maintain consistent plasma levels of that medication.

How to calculate and manage constant rate infusions The Veterinary Nurse
These routes would include delivery by transdermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, intra-articular and intravenous. Intravenous administration of analgesic agents may be timed to be given intermittently or by constant rate infusion.

3 Steps to Calculate IV Drip Rates an infographic Medical eStudy Calculators Ideas of
A constant rate infusion/manually controlled infusion (CRI/MCI) of analgesic drugs is a simple and effective means of improving patient comfort. Various formulations can be used as a constant rate infusion; the protocol chosen depends on the patient and the degree of pain experienced or anticipated.
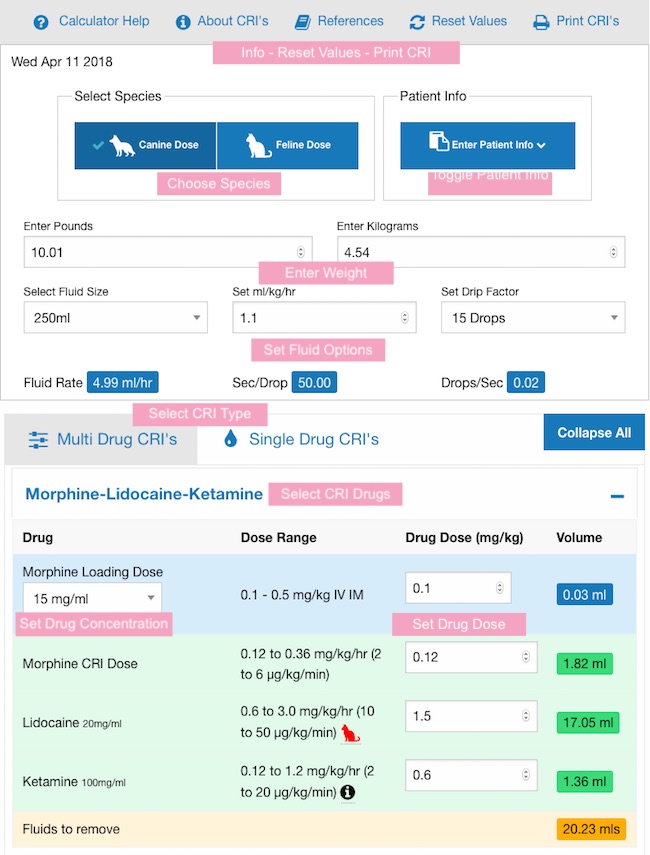
Constant Rate Infusion (CRI) Calculators IVAPM
How to Calculate Dosages* Formula 1By convention, the dosage for many CRI drugs is given as µg/kg/min. The calculations can be confusing since most drugs are available in concentrations of mg/ml and are delivered at a fluid rate of ml/hr. The following formula allows the clinician to "plug in" the numbers and solve for the number of milligrams.

Drug Calculation
Calculators for Emergency and Anesthetic drugs, Constant Rate Infusions (CRI), IV Fluid Rates, Chocolate Toxicity, Calorie requirements for dogs and cats and Unit conversion (including Weight, Temperature, Body Surface Area, mg to ug, cc's to ounces's, cm's to inches).

Insulin Drip Calculations mL/hr Infusion Nursing Practice Problems Dosage Calculations NCLEX
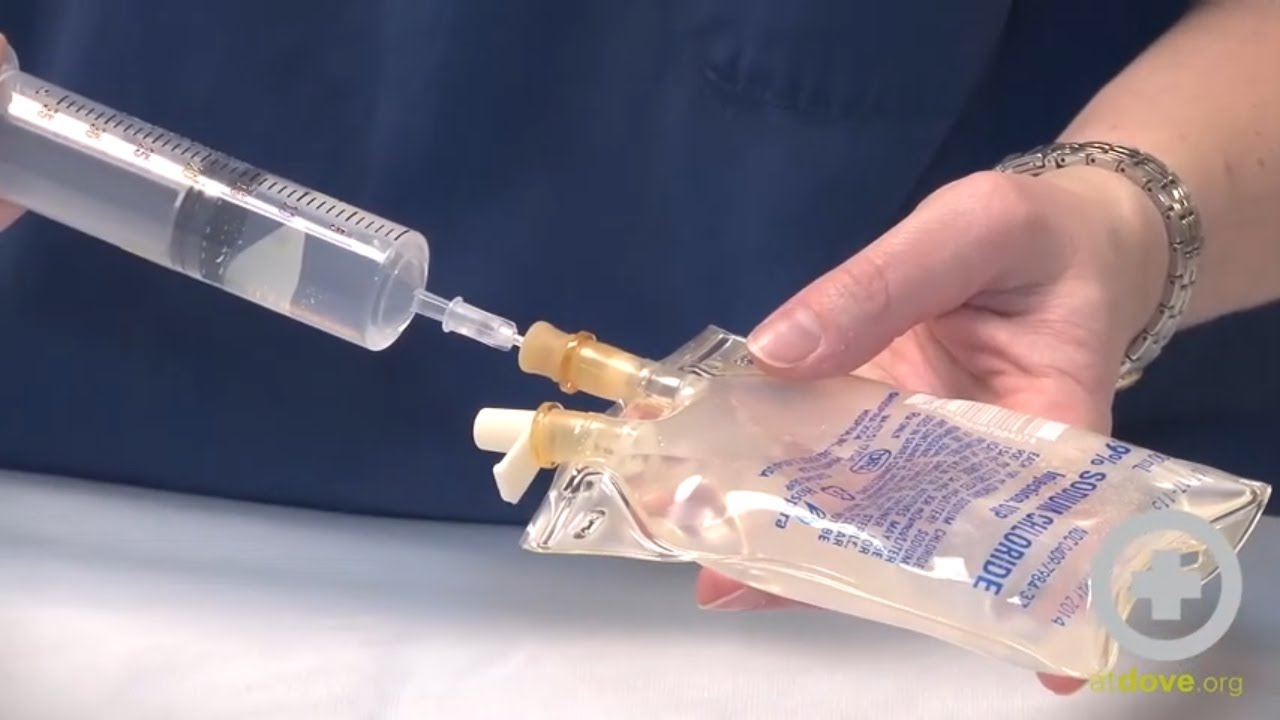
Learn how to calculate a constant rate infusion (CRI) of a drug that has been added a patient's maintenance fluids. A clinical example is provided demonstrating the medical math used to determine the volume of drug to be added to a fluid bag for effective delivery of the CRI within the patient's maintenance fluids.

How to calculate and manage constant rate infusions The Veterinary Nurse
A constant rate infusion/manually controlled infusion (CRI/MCI) of analgesic drugs is a simple and effective means of improving patient comfort. Various formulations can be used as a constant rate infusion; the protocol chosen depends on the patient and the degree of pain experienced or anticipated.

VETgirl Rounds Calculating Constant Rate Infusions (CRIs) in the ICU
A constant rate infusion (CRI) is a medication continuously administered to a patient and is used to maintain consistent plasma levels of that medication. CRIs are commonly administered to patients to achieve appropriate levels of pain management, blood pressure management, sedation, anaesthesia, electrolyte supplementation, insulin, and liquid nutrition via a feeding tube.

How to calculate and manage constant rate infusions The Veterinary Nurse
A constant rate infusion (CRI) is an important part of the treatment journey for many animal patients. CRIs play a key role in pain management, sedation, blood pressure management, electrolyte supplementation, insulin administration, and more.. The calculator allows you to calculate fluid therapy rates for a broad range of scenarios.